 Summer has come to an end and winter is just around the bend. Winter is when I see the most injuries and muscle related complaints. During the winter it is cold outside and potentially icy; we are cold, tense, and our circulation is not great lending to muscle tension and a greater risk of injury. Additionally, winter can be stressful; it involves Holidays, bad weather, multiple family gatherings, travel, and extra expenses.
Summer has come to an end and winter is just around the bend. Winter is when I see the most injuries and muscle related complaints. During the winter it is cold outside and potentially icy; we are cold, tense, and our circulation is not great lending to muscle tension and a greater risk of injury. Additionally, winter can be stressful; it involves Holidays, bad weather, multiple family gatherings, travel, and extra expenses.
Massage therapy is an essential component of your health care routine throughout the year, and the winter & off-season are no exception. Let’s take a look at just a few of the reasons why:
Cold, Snow, & Ice! It is now only a matter of time before we, in the Front Range, have our first snowfall of the season. Then it will begin, the driveway shoveling, tense excursions to and from the car, exercising/training indoors & outdoors: skiing, snowboarding, snowshoeing, walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling in slippery conditions. These are all things that put added stress into our lives, specifically on our musculoskeletal system. Fear no more, for regular massage therapy year-round can help to maintain your muscular flexibility & health, and decrease the chances of injury during the winter.
Winter Sports & Activities Winter sports and activities can be a lot of fun, but there is a definite risk for injury and it is very important that you have a maintenance/massage therapy plan in place to prevent musculotendinous injuries, strains, and sprains from happening. Yet, not all injuries can be prevented, and if you do experience an injury, massage therapy can be a crucial part of your recovery and rehabilitation.
Stress Winter can be a time of tremendous stress. Winter brings Holidays, bad weather, multiple family gatherings, travel, and extra expenses, all things that can cause stress; and let’s not forget that even the things that bring us happiness and joy can also be added stress. Exercise and welcomed life changes are stressful, both mentally and physically. Massage therapy can provide much needed relief, a wonderful place for peace, quite, stillness, healing, and relaxation for the mindbodyspirit.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD, winter blues/depression) During the colder months and shorter days, many people suffer from SAD, a type of depression that occurs at the same time every year. Most people with SAD have symptoms that start in the fall and may continue into the winter months, sapping your energy and making you feel moody. There are also those who may not have SAD, yet experience lethargy and feel gloomy during the winter months. Massage therapy can help soothe and relax your nervous system and bring an overall sense of well-being. Massage therapy decreases stress and anxiety levels, and is very effective in uplifting your mood – massage therapy stimulates the brain to produce endorphins.
Cold & Flu Season Winter is typically the season when many people get ill with colds and/or the flu. Massage therapy can boost your immune system and decrease your chances of getting sick; I almost never get sick! This is another great reason to make massage therapy a regular part of your health care routine year-round! After recovering from a cold or flu, getting a massage can be help eliminate toxins from your system – Just a reminder: As a health care practitioner, I ask that you do not come to your session if you are ill, especially if you have a contagious illness. Massage therapy can exacerbate sickness, and if you come to a session ill, it also puts me and other clients at risk for infection.
So there you have it, these are just a few of the many reasons why massage therapy is essential during the winter & off-season (…& year-round). Receiving massage therapy on a regular basis and throughout the year, gives us a chance to boost our immune system, improve athletic performance, prevent injury, promote healing, manage pain, decrease stress, experience quiet, stillness, and promote relaxation. Massage therapy allows the mind to be silent so that the body can heal from the inside out!
I look forward to seeing you this fall & winter for your continued, regular massage therapy care.
Please checkout the convenient online scheduling on the “Book Now” page!!
Be Well,
Maia
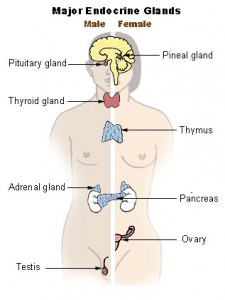 The endo…what? I’ll give you a hint, it’s not what you do when you go over your handlebars. In simplest terms, it is a system of glands, each of which secretes a type of hormone directly into the bloodstream to regulate the body. The endocrine system is in contrast to the exocrine system, which secretes its chemicals using ducts. The endocrine system influences almost every cell, organ, and function in our bodies. It is instrumental in regulating mood, tissue function, metabolism, and reproductive processes to name a few.
The endo…what? I’ll give you a hint, it’s not what you do when you go over your handlebars. In simplest terms, it is a system of glands, each of which secretes a type of hormone directly into the bloodstream to regulate the body. The endocrine system is in contrast to the exocrine system, which secretes its chemicals using ducts. The endocrine system influences almost every cell, organ, and function in our bodies. It is instrumental in regulating mood, tissue function, metabolism, and reproductive processes to name a few.![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=edd46bea-c96d-4e6f-ae0f-5f8b7ea9e215)
 Stress is a fact of life and a necessity in many cases but left unaddressed, stress can wreak havoc on your body systems and interfere with the intelligent workings of your body. Simply put, general health will be impaired and ill effects unavoidable.
Stress is a fact of life and a necessity in many cases but left unaddressed, stress can wreak havoc on your body systems and interfere with the intelligent workings of your body. Simply put, general health will be impaired and ill effects unavoidable.